Understanding the 4 Types of Multiple Sclerosis (MS):
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) presents in several forms, each with distinct characteristics. The main types of MS include:
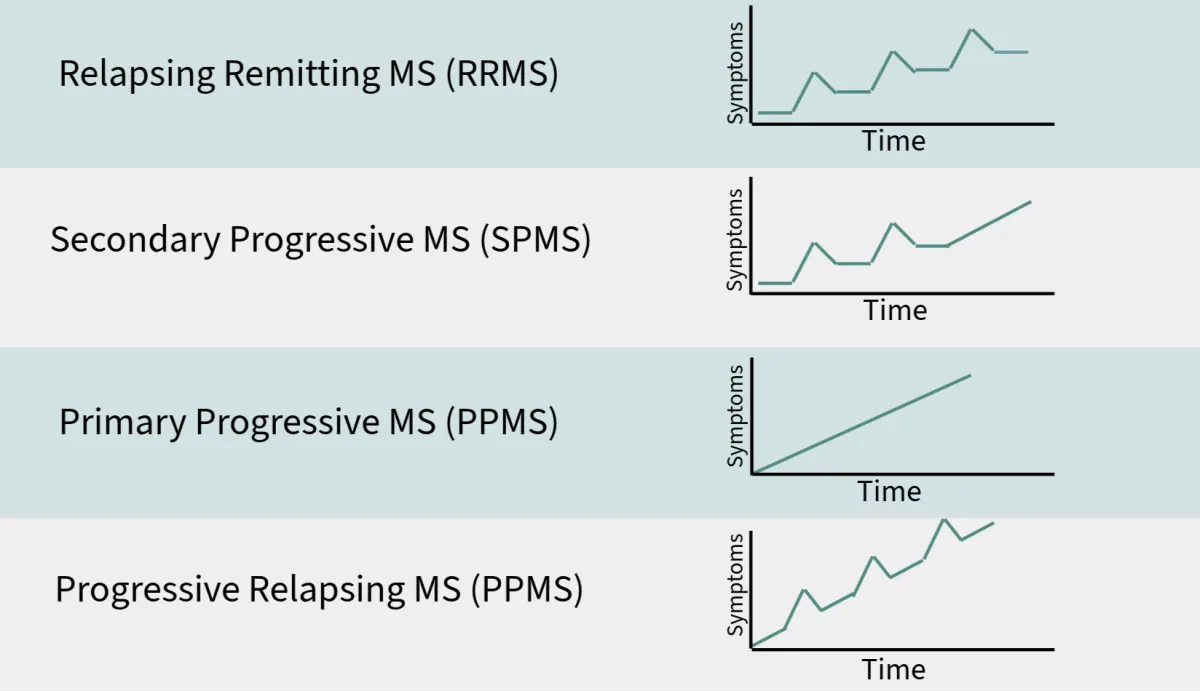
Relapsing-Remitting MS (RRMS): This is the most common form of MS, characterized by unpredictable flare-ups (relapses) followed by periods of partial or complete recovery (remissions). Between relapses, individuals may experience stable or improving symptoms.
Secondary-Progressive MS (SPMS): After an initial period of relapsing-remitting symptoms, some individuals with RRMS may transition to SPMS, marked by a gradual worsening of symptoms and disability, with or without relapses or remissions.
Primary-Progressive MS (PPMS): In PPMS, symptoms worsen steadily from the onset, without distinct relapses or remissions. This form is less common than RRMS or SPMS and tends to lead to more rapid disability progression.
Progressive-Relapsing MS (PRMS): PRMS is characterized by a steady worsening of symptoms from the beginning, with occasional relapses and periods of stability.
